The early bird gets the worm. Get ready for the coming season.
Casea Beneficial Nematode
Casea Beneficial Nematode
Не удалось загрузить сведения о доступности самовывоза
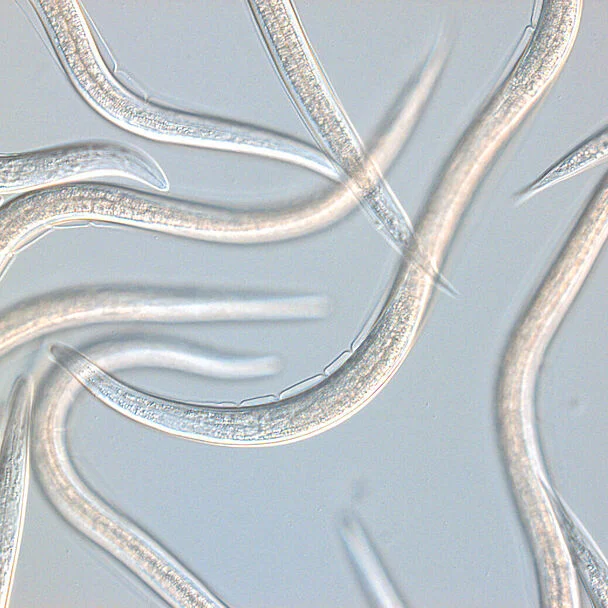
Scientific name: Steinernema carpocapsae.
Nematode species of the genus Steinernema form symbiotic relationships with bacteria that are crucial to the survival of the nematodes for food and reproductive life cycles. The bacteria are known to be pathogenic to a wide range of insects.
The entomopathogenic nematodes enter soil dwelling insects and larvae through natural openings to deposit the bacteria which feed on the rich lifeblood medium of the host. The bacteria grow and release toxins and exoenzymes, effectively infecting and killing the insect or larva host within 24 to 48 hours.
The nematodes feed on the multiplying and growing bacteria and the remains of the host converted into a nutrient source by the bacteria and reproduce themselves and grow.
When there is insufficient nutrient, the nematodes enter a non feeding, developmentally arrested, free living stage in which they can survive in the soil environment until they find a new host.
Steinernema carpocapsae is a generalist parasite and an ambush forager, standing on its tail in an upright position near the soil surface and attaching to passing hosts, even capable of jumping. This species of nematode is thought to be especially effective when applied against highly mobile surface adapted insects though some below ground insects are also controlled by this nematode.
Because nematodes and their bacterial complex kill and eliminate plant pests quickly, they have been widely adapted for use as a biological control agent in agricultural open field and greenhouse crops.
*Exercise educated caution so beneficial and endemic insects and their larvae are not affected.
Use for:
-
Biological control of various agricultural insect pests in stone fruits, outdoor field vegetables and urban landscaping trees.
- Can be applied with regular spray equipment.
-
Highly soluble biodegradable formulation with long shelf life.
-
Caterpillars (Lepidoptera): Armyworms (Spodoptera spp.), Cotton bollworm (Helicoverpa armigera), Corn earworm (Helicoverpa zea), Tomato looper (Chrysodeixis chalcites), Cutworms (Agrotis spp.), Silver Y moth (Autographa gamma), Box tree moth (Cydalima perspectalis), South American palm borer (Paysandisia archon).
-
Beetle larvae (Coleoptera): Flatheaded root borer (Capnodis tenebrionis), Wireworms/ Click beetles(Agriotes spp.), Flea beetles (Phyllotreta spp.).
-
Beetle larvae and adults (Coleoptera): Red palm weevil (Rhynchophorus ferrugineus), South American palm weevil (Rhynchophorus palmarum).
- Crane flies/ leatherjackets (Tipulidae): Tipula spp.
- Bugs (Heteroptera): Sycamore lace bug (Corythucha ciliata).
Mode of action:
The nematodes enter the pest and release symbiotic bacteria into the pest body cavity. These bacteria convert the host tissue into a food source, on which nematodes feed and develop then reproduce inside the host. The bacterial toxins kill the pest within a few hours to days after infection.
Visually, infected pest insects in the root zone turn yellow to brown but may be difficult to find, due to rapid degradation. Infected foliar pests simply fall to the ground.
Product specifications:
| Pack size | 3000 million - 4 sachets of 750 million in a box. |
| Developmental stage | Infective third stage larvae (L3). |
| Concentration | 86% Steinernema carpocapsae, 14% inert biodegradable carrier. |
Preparation for use:
- Remove the sachets from the box and keep them at room temperature for 30 minutes.
- Empty the contents of the sachets into a bucket containing at least 2 litres of water per sachet (water temperature: 15°C to 20°C / 59°F to 68°F).
- Stir well and leave the contents to soak for five minutes.
- Stir again and pour the contents of the bucket into the half filled spray tank (except when tank mixing with a compatible product).
- Maintain agitation of mixture in the tank (e.g. with a recirculation pump).
- Fill the spray tank with the required amount of water.
- If tank mixing with a compatible product, add Casea at the end to a fully filled tank.
- Apply directly after preparation of spray solution.
Application:
- Nematodes can be applied using a watering can, an airblast sprayer, a vehicle mounted spray unit, a backpack sprayer or through a sprinkler system.
- To avoid blockage, all filters should be removed, especially if finer than 0.3 mm
(50 mesh). - Use a maximum pressure of 20 bar/ 290 psi (on nozzle).
- The spray nozzle opening should be at least 0.5 mm (500 microns / 35 mesh), preferably high flow rate cone nozzle types.
- Continuous mixing should take place to prevent nematodes sinking to the bottom of the spray tank.
- Avoid sprayers equipped with centrifugal or piston pumps.
- Water tank temperature must not exceed 25°C / 77°F and pH must be between 4 and 8.
- Distribute the spraying solution evenly over the soil or growing medium surface.
Application through irrigation systems:
- Pressure compensated irrigation systems are recommended. If not available, spray or drench applications are recommended.
- Spray the solution as soon as it is prepared and within a short timeframe. Do not store mixed suspensions.
Storage:
- See expiry date on the box. On average product can be stored for 2 to 3 months.
- Refrigerate at a temperature of 2°C to 6°C / 35°F to 43°F in a ventilated refrigerator or cold room.
- Upon receipt, take boxes out of the insulating shipment packaging. Keep in a dark, temperature adjusted room until use.
Caution:
- Pesticides can have direct or indirect effects on biological solutions.
- As a general rule for tank mixing, always add the nematodes to a fully filled tank containing the compatible product.
- The product is safe for most beneficial insects and mites, but can have some effect on a few when in direct contact with foliar applied nematodes.
- Only use products that are permitted in your country or state and crop.
Share